
The digitalisation of the customer journey has enabled the transformative integration of embedded finance solutions around the globe, and that has extended to lending. Embedded credit assessment leverages alternative data like open banking and behavioural analytics to streamline the risk decisioning process within the application.

Imagine a world where the fabric of lending is woven with threads of data, where financial transactions and behavioural analytics support credit risk decisions, making credit fairer and more inclusive. This is the reality of embedded credit assessment, where alternative data sources like open banking and behavioural analytics can open opportunities for more people to seamlessly access the credit products meaningful to them.
Embedded finance is experiencing remarkable growth. The global embedded finance market was valued at approximately $58 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach around $730.5 billion by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 29% during the forecast period from 2023 to 2032. This rapid expansion is driven by the increasing adoption of digital payments, the demand for frictionless financial services, and innovations in fintech such as APIs and digital payments.
Embedded finance refers to the seamless integration of financial services into non-financial platforms, products, or services. This integration enables consumers to access various financial services, such as payments, lending, insurance, and investment, directly within the platforms they are already using. Instead of going through traditional banking channels, users can complete financial transactions as part of their everyday activities, making financial services more accessible and convenient.
Imagine you are using a ride-sharing app like Uber or Lyft to book a ride to work. The app not only helps you find a driver and track your ride in real-time but also seamlessly handles the payment process.
Embedded credit assessment is a revolutionary approach that integrates credit evaluation and decisioning processes directly into platforms where financial transactions and interactions occur. By leveraging alternative data sources, it enables a more comprehensive and accurate assessment of a borrower’s creditworthiness. This method streamlines the loan approval process, providing real-time insights and reducing the reliance on traditional credit scores. For lenders, it means faster, data-driven decision-making and improved risk management, while for consumers, it offers greater access to credit and personalized financial products. Ultimately, embedded credit assessment transforms the landscape of lending, making it more inclusive and efficient.
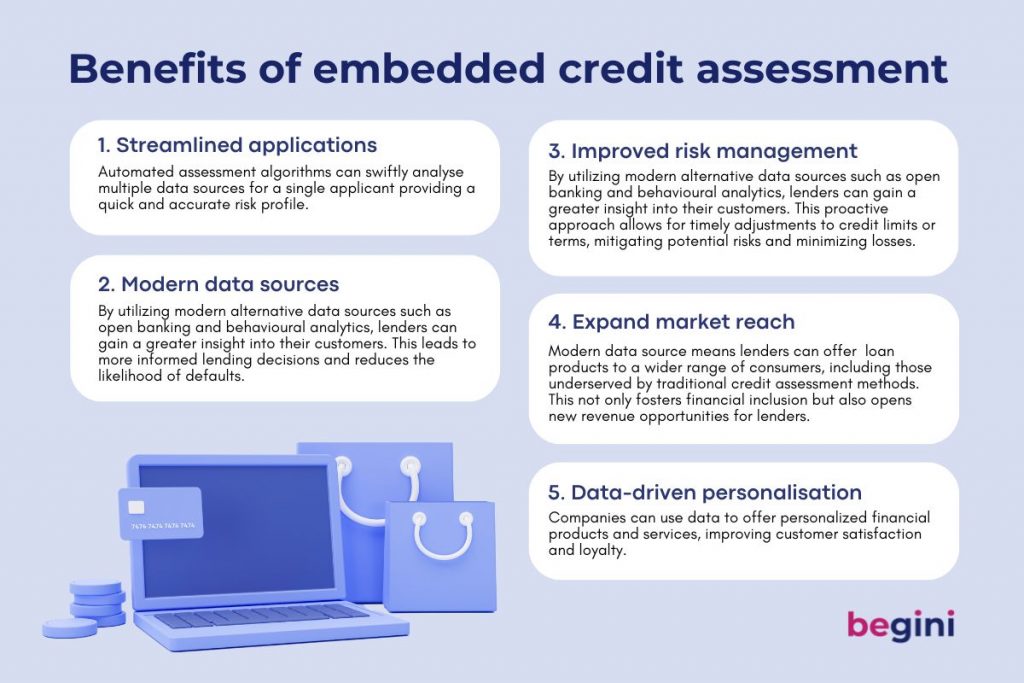
Embedded credit assessment can bring numerous advantages to lenders, revolutionizing the way they evaluate borrowers and manage risk
1. Streamlined applications
By integrating credit assessment directly into their systems or platforms, lenders can streamline and expedite the loan approval process. Automated assessment algorithms can swiftly analyse multiple data sources for a single applicant, such as financial data, credit history, behavioural analytics and other relevant factors, providing a quick and accurate risk profile. This efficiency translates into reduced processing times, enabling lenders to cater to a larger number of applicants while ensuring a more seamless customer experience.
2. Modern data sources enhance accuracy
By utilizing modern alternative data sources such as open banking and behavioural analytics, lenders can gain a more comprehensive and precise understanding of a borrower’s creditworthiness. This leads to more informed lending decisions and reduces the likelihood of defaults.
Traditional methods often rely on manual evaluations that can be subjective and prone to human errors. By employing advanced data analytics and machine learning models, lenders can assess a borrower’s creditworthiness more objectively and comprehensively. This leads to more informed lending choices, mitigating the likelihood of default and reducing the overall credit risk in the lender’s portfolio.
3. Improved Risk Management
Continuous access to real-time data enables lenders to monitor borrowers’ financial behaviours throughout the loan term. This proactive approach allows for timely adjustments to credit limits or terms, mitigating potential risks and minimizing losses.
4. Expanded Market Reach
With a more nuanced understanding of creditworthiness, lenders can offer tailored loan products to a wider range of consumers, including those who may have been underserved by traditional credit assessment methods. This not only fosters financial inclusion but also opens new revenue opportunities for lenders.
5. Data-Driven Personalization
Companies can use data to offer personalized financial products and services, improving customer satisfaction and loyalty.
6. Revenue Opportunities
Businesses can create new revenue streams by offering financial products and services directly within their platforms.
1. API Integration
At the core of embedded finance is the use of Application Programming Interfaces (APIs). Financial service providers develop APIs that allow their services to be integrated into third-party platforms.
2. Partnerships and Collaboration
Companies collaborate with financial institutions, fintech companies, and technology providers to offer embedded financial services. These partnerships are essential for providing secure, compliant, and reliable financial products within non-financial ecosystems.
3. User Experience Enhancement
By embedding financial services directly into existing user experiences, companies can reduce friction and enhance customer satisfaction. For example, an e-commerce platform can offer instant financing options at checkout, allowing customers to buy now and pay later without leaving the site.
4. Data Utilization
Embedded finance leverages data from various sources to provide personalized financial solutions. For instance, an online marketplace might use transaction data to offer tailored lending products to sellers, based on their sales history and performance, or they might offer the borrower to share or create behavioural data through a gamified character assessment which uses psychometrics.
The possible uses cases for embedded lending are seemingly endless, some common use cases that we are already seeing today include:
1. Point-of-Sale (POS) Financing
E-commerce Platforms or In-store Financing: Retailers and online marketplaces offer customers the option to finance their purchases at checkout through “buy now, pay later” services, either through a third-party provider or the retailers own financing solution. Physical stores can integrate lending options directly into their payment systems, enabling customers to access financing for larger purchases on the spot.
2. B2B Financing
Supplier Financing: Platforms that facilitate transactions between businesses, such as supply chain management systems, integrate lending options to help suppliers finance their inventory purchases. For example, Amazon offers financing to its third-party sellers to help them stock up on inventory.
Invoice Financing: Business management platforms can embed lending options that allow businesses to borrow against their unpaid invoices, improving their cash flow management.
3. Gig Economy and Freelance Platforms
Cash Advances for Gig Workers: Ride-sharing and delivery service platforms offer cash advances or short-term loans to their drivers and couriers, helping them cover immediate expenses or vehicle maintenance costs.
4. Healthcare Financing
Medical Billing: Healthcare providers partner with fintech companies to offer patients financing options for medical bills directly through their billing systems.
5. Automotive Financing
Car Dealerships: Automotive sales platforms integrate financing options directly into their websites or in-store systems, enabling customers to get pre-approved for loans or lease options as they shop for vehicles.
7. Education and Learning Platforms
Student Financing: Online learning platforms and educational institutions offer financing options for course fees and educational materials.
Integrating modern data such as open banking data and behavioural analytics into embedded lending decisioning can revolutionize the accuracy and efficiency of credit assessments. Open banking data provides lenders with real-time access to a consumer’s financial transactions, including income, spending habits, and account balances. This comprehensive financial snapshot allows for more precise risk assessments, enabling lenders to make informed decisions quickly.
Behavioural analytics further enhance this process by giving insight into a borrower’s personality traits and risk preferences. Psychometric assessments evaluate characteristics such as honesty, discipline, and risk tolerance, which are predictive of financial behaviour. Studies have shown that these assessments, can significantly improve the predictive power of credit models.
By leveraging these diverse data sources, lenders can develop a more holistic view of a borrower’s creditworthiness, leading to more personalized and fair lending products. This approach not only reduces risk for lenders but also expands access to credit for consumers who might have been underserved by traditional methods.
In conclusion, embedded credit assessment empowers lenders with efficient, accurate and proactive tools to make informed lending decisions, ultimately resulting in better risk management, improved customer satisfaction, and healthier financial outcomes for the lending institution.